[Data Structure & Alogrithm] Cpp Coing Test Tip
📝 <algorithm>
📌 find
- 범위 안에 원하는 값을 찾아준다.
- ex) 벡터 내에 특정 값이 있는지 확인할 때 사용.
- 찾고자하는 값이 있으면, 해당 위치를 가리키는 이터레이터 반환.
- 찾고자하는 값이 없으면, 원소의 끝을 가리키는 end() 반환.
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
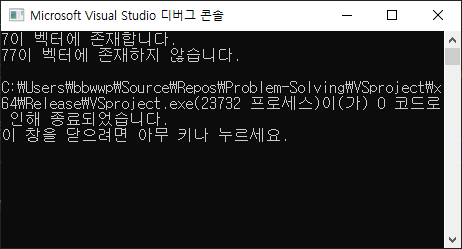
vector<int> v = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
int num = 7;
if (find(v.begin(), v.end(), num) != v.end())
cout << num << "이 벡터에 존재합니다.\n";
else
cout << num << "이 벡터에 존재하지 않습니다.\n";
num = 77;
if (find(v.begin(), v.end(), num) != v.end())
cout << num << "이 벡터에 존재합니다.\n";
else
cout << num << "이 벡터에 존재하지 않습니다.\n";
return 0;
}
📌 sort
📌 reverse
📝 <string>
📌 substr
- substr을 사용하면, 문자열을 원하는 크기로 자를 수 있다.
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
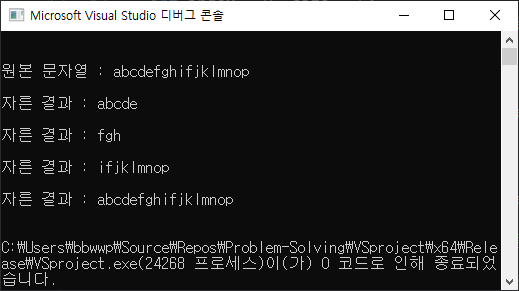
string str = "abcdefghifjklmnop";
cout << "원본 문자열 : " << str + "\n\n";
// 인덱스 0부터 5개만큼 자른다.
int index = 0, size = 5;
cout << "자른 결과 : " << str.substr(index, size) + "\n\n";
// 인덱스 5부터 3개만큼 자른다.
index = 5, size = 3;
cout << "자른 결과 : " << str.substr(index, size) + "\n\n";
// 이렇게 인덱스만 주면, 인덱스부터 끝까지 자른다.
index = 8;
cout << "자른 결과 : " << str.substr(index) + "\n\n";
// size가 문자열 크기를 초과하면, 끝까지 자른다.
index = 0, size = 99999999;
cout << "자른 결과 : " << str.substr(index, size) + "\n\n";
return 0;
}
📌 find
📌 erase
📌 stoi, stol, stoll
📌 getline
📌 replace
📝 <set>
- 중복된 원소를 담지 않는 자료구조다.
- cpp set은 min heap으로 구현되어있다.
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main(){
set<int> s;
s.insert(-1);
s.insert(11);
s.insert(-34);
s.insert(122);
s.insert(83);
cout << *s.begin() << endl; // 내부구조가 min heap이므로 -34 출력
cout << *s.rbegin() << endl; // 내부구조가 min heap이므로 122 출력
}
🔎 출처 & 더 알아보기

